Understanding the difference between water-cooled and air-cooled systems
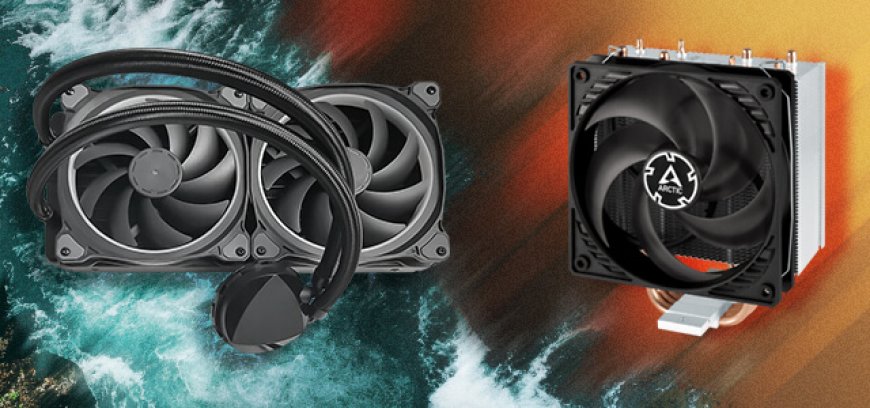

Understanding the difference between water-cooled and air-cooled systems
Introduction to Cooling Systems
Definition of Cooling Systems
Importance of Efficient Cooling
Introduction to Cooling Systems
When it comes to keeping things chill, cooling systems play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures for various applications. Whether it's your computer, car engine, or industrial machinery, efficient cooling is key to preventing overheating and ensuring smooth operations. Proper maintenance and regular monitoring of cooling systems are necessary to ensure they are functioning effectively. Without efficient cooling, the risk of equipment failure due to overheating increases significantly. By investing in high-quality cooling systems and implementing proper cooling strategies, businesses can avoid costly repairs and downtime caused by heat-related issues.
Definition of Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are designed to remove excess heat generated by a device or machinery to maintain its operating temperature within safe limits. By dissipating heat, cooling systems help prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Proper maintenance of cooling systems is also key in ensuring their effectiveness. Regular inspections, cleaning, and servicing can help identify any potential issues before they escalate into costly problems. By investing in high-quality cooling systems and implementing proper cooling strategies, businesses can not only avoid expensive repairs and downtime but also prolong the lifespan of their equipment.
Importance of Efficient Cooling
Efficient cooling is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of equipment. Inadequate cooling can lead to overheating, which can cause components to wear out faster and even result in system failures. Choosing the right cooling solution is crucial for maintaining efficiency and reliability. When it comes to efficient cooling, there are various methods to consider, with water-cooled systems being one popular option. These systems offer a more effective way to dissipate heat compared to air cooling, making them ideal for high-performance equipment. By utilizing water as a coolant, these systems can effectively regulate temperatures and prevent overheating, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
How Water-Cooled Systems Work
Water-cooled systems take a liquid approach to cooling, using water as a primary coolant to dissipate heat generated by the system. Water-cooled systems offer a more efficient method of heat dissipation compared to air cooling systems. By using water as a coolant, these systems are able to maintain optimal temperatures and prevent overheating, ensuring the longevity of high-performance equipment. The liquid cooling approach of water-cooled systems allows for precise temperature regulation, making them an ideal choice for demanding applications.
Components of a Water-Cooled System
A typical water-cooled system consists of a water block, pump, radiator, fan, and tubing. The water absorbs heat from components through the water block, circulates to the radiator for cooling, and returns to the system to repeat the process. Water-cooled systems offer a more efficient and effective method of cooling compared to air-cooled systems. By using water as a medium to transfer heat away from components, water-cooled systems can achieve more precise temperature control and better overall performance. The closed-loop nature of water cooling also helps to minimize noise levels, making it a popular choice for high-performance computing systems.
Process of Heat Transfer in Water-Cooled Systems
In a water-cooled system, heat is transferred from components to the circulating water, which carries it away to the radiator for dissipation. This continuous cycle helps maintain optimal temperatures and prevents overheating. While water-cooled systems are known for their efficiency in dissipating heat, air-cooled systems offer a simpler and more cost-effective solution for many users. Air-cooled systems do not require the use of a pump or tubing like water-cooled systems, making them easier to install and maintain. Additionally, air-cooled systems are often preferred for smaller computing setups where space may be limited.
How Air-Cooled Systems Work
Air-cooled systems take a breezy approach to cooling, relying on airflow to dissipate heat generated by the system. One key advantage of air-cooled systems is their simplicity. Without the need for complex water pumps or tubing, installation and maintenance are straightforward and hassle-free. This makes air-cooled systems a popular choice for beginners or those looking for a low-maintenance cooling solution. Additionally, air-cooled systems are often more cost-effective than their water-cooled counterparts, making them a budget-friendly option for many users.
Components of an Air-Cooled System
An air-cooled system typically includes heat sinks, fans, and vents. Heat sinks absorb heat from components and transfer it to the surrounding air, while fans help to circulate air for efficient heat dissipation. When comparing air-cooled systems to water-cooled systems, it is important to consider the simplicity and ease of maintenance that air-cooled systems offer. With fewer components and no need for a water pump or tubing, air-cooled systems are generally easier to install and maintain. Additionally, air-cooled systems are typically more compact and lightweight, making them a practical choice for users with limited space or mobility constraints.
Process of Heat Dissipation in Air-Cooled Systems
In an air-cooled system, heat is transferred from components to the heat sink, where it is dissipated into the air through convection. The airflow created by fans helps to carry away the heat, keeping the system cool and running smoothly. While air-cooled systems may be more compact and lightweight, they may not offer the same level of cooling performance as water-cooled systems. However, for users with limited space or mobility constraints, the practicality of air-cooled systems may outweigh the potential performance benefits of water-cooled systems. Ultimately, the choice between the two will depend on the specific needs and priorities of the user.
Performance Comparison: Water-Cooled vs. Air-Cooled Systems
When it comes to choosing between water-cooled and air-cooled systems, each has its own set of pros and cons to consider. When deciding between water-cooled and air-cooled systems, it's important to consider factors such as the level of maintenance you are willing to commit to, the complexity of the setup process, and the potential risks involved. Water-cooled systems may offer superior cooling performance, but they come with the added responsibility of regular maintenance and the possibility of leaks. On the other hand, air-cooled systems are easier to install and require less upkeep, making them a more convenient option for those looking for a simpler solution.
Pros and Cons of Water-Cooled Systems
Water-cooled systems are known for their superior cooling performance and efficiency, making them ideal for high-power applications. However, they require more maintenance, can be complex to set up, and pose a risk of leaks if not properly installed. When considering cost, it's important to factor in not just the initial installation expenses, but also the long-term maintenance costs associated with each type of cooling system. Water-cooled systems may have higher upfront costs and require more frequent maintenance, but they can offer greater energy efficiency and potentially lower operating costs in the long run. On the other hand, air-cooled systems may be more budget-friendly initially, but their lower cooling performance could result in higher energy bills over time. Efficiency-wise, water-cooled systems have the advantage of being able to dissipate heat more effectively, leading to better overall performance in demanding environments.
Pros and Cons of Air-Cooled Systems
Air-cooled systems are simpler to install, require less maintenance, and are generally more cost-effective. However, they may not provide the same level of cooling performance as water-cooled systems, especially in high-heat environments. While air-cooled systems may be more cost-effective upfront, water-cooled systems offer long-term savings in terms of energy efficiency. The ability of water-cooled systems to dissipate heat more effectively can result in lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs over time. Additionally, water-cooled systems are often preferred in demanding environments where consistent and efficient cooling is crucial for optimal performance.
Cost Considerations and Efficiency
When it comes to cost considerations and efficiency, the debate between water-cooled and air-cooled systems heats up. In terms of initial investment and operating costs, air-cooled systems typically come out on top. They are generally more affordable to install and maintain compared to their water-cooled counterparts. However, water-cooled systems can offer better long-term energy efficiency, potentially offsetting their higher upfront costs in the right circumstances. When it comes to maintenance, air-cooled systems also have the upper hand. They typically require less upkeep and are easier to troubleshoot, saving both time and money in the long run. On the other hand, water-cooled systems may have higher operating costs due to the need for water treatment and regular maintenance of cooling towers. Despite these ongoing expenses, water-cooled systems are known for their superior energy efficiency, which can lead to significant savings on utility bills over time.
Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Air-cooled systems are like the budget-friendly sneakers you grab on sale, while water-cooled systems resemble the high-end designer shoes that require a bit more investment. Air-cooled systems are cheaper to purchase and simpler to install, making them a popular choice for cost-conscious consumers. On the other hand, water-cooled systems may have a higher initial investment due to the additional components required for water circulation and cooling towers. Operating costs, such as water usage and maintenance, also tend to be higher for water-cooled systems.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
When it comes to energy efficiency ratings, water-cooled systems often have the upper hand. Water is a more effective heat transfer medium than air, allowing water-cooled systems to achieve higher efficiency levels. This can result in lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs over the system's lifespan. Air-cooled systems, while generally less efficient, can still be a good choice for applications where water availability or cost is a concern.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Maintenance requirements and longevity play a crucial role in determining the overall performance of cooling systems. Whether you choose a water-cooled or air-cooled system, proper maintenance is key to maximizing efficiency and extending the system's lifespan. When it comes to air-cooled systems, maintenance requirements are generally less intensive compared to water-cooled systems. However, regular cleaning of air filters, checking for any debris or blockages, and ensuring proper airflow are still necessary to ensure optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance tasks for air-cooled systems can result in reduced cooling capacity, higher operating temperatures, and potential system failures.
Maintenance Tasks for Water-Cooled Systems
Water-cooled systems require regular maintenance to prevent issues like scale buildup, corrosion, and microbiological growth in the cooling towers. Tasks such as water treatment, cleaning of heat exchangers, and monitoring water quality are essential for keeping water-cooled systems running smoothly. Failure to maintain these systems properly can lead to decreased efficiency, increased energy consumption, and costly repairs.
Maintenance Tasks for Air-Cooled Systems
Air-cooled systems are generally less maintenance-intensive compared to water-cooled systems. Regular inspections of fans, filters, and coils are necessary to ensure proper airflow and heat transfer. Keeping the outdoor unit clean and free of debris is crucial for optimal performance. While air-cooled systems may require less maintenance overall, neglecting routine tasks can still result in decreased efficiency and potential breakdowns.
Environmental Impact of Cooling Systems
In today's environmentally conscious world, the impact of cooling systems on the planet is a significant consideration for consumers and businesses alike. Understanding the eco-friendly aspects and sustainability factors of water-cooled and air-cooled systems can help make informed decisions that align with green practices.
Eco-Friendly Aspects of Water-Cooled Systems
Water-cooled systems are often touted for their eco-friendly design, as they use water as a natural and efficient heat transfer medium. By leveraging water's superior thermal properties, these systems can reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to air-cooled alternatives. Additionally, water-cooled systems can potentially utilize alternative water sources such as rainwater or treated wastewater, further reducing their environmental impact.
Sustainability Factors of Air-Cooled Systems
Air-cooled systems offer sustainability benefits in terms of water conservation and ease of installation. Unlike water-cooled systems, air-cooled systems do not require significant water usage for cooling purposes, making them a more water-efficient option in regions facing water scarcity. Additionally, the simpler installation process of air-cooled systems can reduce construction-related environmental impacts and lead to lower overall carbon footprint.
What's Your Reaction?