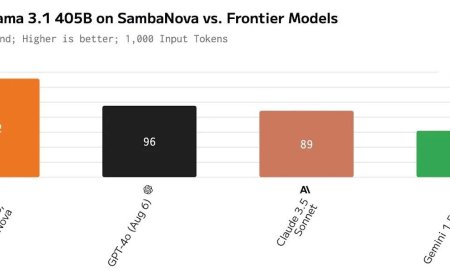
Predicting the Limits of Moores Law for Future CPU Innovation
Predicting the Limits of Moores Law for Future CPU Innovation
Advancements in computing technology have long been driven by the guiding principle of Moore's Law, which posits that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in processing power. This law, formulated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in 1965, has been instrumental in shaping the trajectory of CPU innovation and fueling the rapid evolution of computing devices. However, as transistor sizes approach atomic scales and technological limitations emerge, questions arise about the sustainability of Moore's Law for future CPU development. In this article, we delve into the factors influencing the limits of Moore's Law, explore the challenges in maintaining its pace, discuss alternative strategies to overcome these limitations, and consider the implications of reaching the threshold of Moore's Law for the tech industry as a whole. Additionally, we look ahead to the future prospects of CPU innovation beyond Moore's Law and the potential avenues for continued advancement in computing technology.
# Introduction to Moore's Law and Its Impact on CPU Innovation
Moore's Law has been the guiding light for the semiconductor industry, predicting that the number of transistors on a chip would double approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. Despite the remarkable advancements facilitated by Moores Law, the semiconductor industry is now facing increasing difficulties in maintaining the pace of transistor scaling. As transistors continue to shrink to nanoscale sizes, issues such as leakage currents, heat dissipation, and quantum effects are becoming more pronounced, posing significant hurdles to further progress. These challenges have prompted researchers and industry experts to explore alternative strategies to sustain the momentum of CPU innovation beyond the traditional confines of Moores Law.
## Defining Moore's Law
Coined by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in 1965, Moore's Law has been the driving force behind the rapid advancements in CPU performance and efficiency over the past decades. As researchers and industry experts grapple with the limitations of Moores Law, the need for innovative solutions becomes increasingly urgent. The traditional approach of simply scaling down transistor sizes is no longer sufficient to sustain the pace of CPU innovation. This shift in focus towards alternative strategies reflects a pivotal moment in the evolution of computing technology.
## Historical Significance of Moore's Law in CPU Development
From the early days of single-core processors to the current era of multi-core powerhouses, Moore's Law has set the stage for relentless innovation in the world of computing, shaping how we work and play. As the industry grapples with the limitations of scaling down transistor sizes, researchers and engineers are exploring new avenues to continue the pace of CPU innovation. This shift in focus towards alternative strategies marks a turning point in the evolution of computing technology, challenging the long-standing dominance of Moores Law in driving progress.
# Factors Influencing the Limits of Moore's Law
As we push the boundaries of Moore's Law, several challenges loom large, threatening to slow down the exponential growth we have come to expect. One of the key factors influencing the limits of Moores Law is the diminishing returns of scaling down transistor sizes. As transistors become smaller and smaller, the challenges of leakage currents and quantum effects become more pronounced, making it increasingly difficult to maintain the same rate of improvement in performance and efficiency. Additionally, the increasing complexity of designing and manufacturing these tiny transistors adds another layer of difficulty, requiring innovative solutions to overcome these obstacles.
## Shrinking Transistor Sizes
The race to cram more transistors onto a chip is hitting physical limits as we approach atomic scales, posing a challenge to the traditional Moore's Law trajectory. As transistors continue to shrink, the challenges of leakage currents and quantum effects become more pronounced, making it increasingly difficult to maintain the same rate of improvement in performance and efficiency. The industry is now faced with the daunting task of finding new ways to overcome these obstacles in order to keep pace with the demands of modern technology. Additionally, the increasing complexity of designing and manufacturing these tiny transistors adds another layer of difficulty, requiring innovative solutions to ensure continued progress in the field of semiconductor technology.
## Heat Dissipation Challenges
With more transistors densely packed on a chip, heat dissipation becomes a significant hurdle, affecting performance and reliability if not effectively managed. One key challenge that the industry must address is the increasing power consumption of these densely packed transistors, which can lead to overheating and reduced efficiency. This not only impacts the performance of the chips but also raises concerns about the environmental impact of such high energy consumption. Finding innovative ways to improve energy efficiency and heat dissipation will be crucial in overcoming these challenges and ensuring the continued advancement of semiconductor technology.
## Manufacturing Complexity and Costs
As the complexity of manufacturing chips increases to keep up with Moore's Law, so do the costs, requiring substantial investments in cutting-edge technologies and facilities. As the demand for smaller, faster, and more powerful chips continues to grow, the pressure to innovate in energy efficiency and heat dissipation becomes even more critical. Manufacturers must find ways to balance the need for increased performance with the need to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact. This delicate balance will be key in ensuring the future success of semiconductor technology.
# Technological Challenges in Sustaining Moore's Law for Future CPU Development
Looking ahead, the road to sustaining Moore's Law faces formidable obstacles that require innovative solutions to keep the momentum going. As manufacturers strive to push the boundaries of semiconductor technology, they must also grapple with the increasing demands for energy efficiency and sustainability. The pressure to deliver higher performance while minimizing environmental impact adds another layer of complexity to the already challenging task of sustaining Moores Law. Finding a delicate balance between these competing priorities will be crucial for the future viability of CPU development.
## Physical Limits of Semiconductor Technology
The laws of physics dictate that we can only miniaturize transistors so much before quantum effects and other physical constraints come into play, signaling a potential roadblock for future chip developments. As the semiconductor industry grapples with the physical limits of transistor miniaturization, the need for innovative solutions becomes increasingly urgent. The emergence of quantum effects and the challenges they pose highlight the necessity for alternative approaches to sustain the pace of CPU development.
## Quantum Effects and Quantum Tunneling
As transistors shrink to nanoscale dimensions, quantum effects such as tunneling become more pronounced, challenging the reliability and predictability of traditional computing architectures. One potential solution to address the challenges posed by quantum effects and tunneling is the development of quantum computing. By harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics, quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize computing by performing complex calculations at speeds unimaginable with traditional computers. Additionally, research into new materials and structures that can mitigate the impact of quantum effects on transistor performance is crucial for advancing CPU development in the face of these challenges.
# Alternative Approaches to Overcoming Moore's Law Limitations
To navigate the impending limits of Moore's Law, researchers and engineers are exploring novel strategies and technologies to drive CPU innovation forward. As Moores Law reaches its limits, the need for alternative approaches to continue advancing CPU development becomes increasingly urgent. Researchers and engineers are actively exploring innovative strategies, such as 3D chip stacking and nanotechnology, to overcome these limitations and drive computing innovation forward. By embracing new materials and technologies, the tech industry can push the boundaries of performance and capabilities, ensuring continued growth and progress in the face of evolving challenges.
## 3D Chip Stacking
By stacking multiple layers of chips on top of each other, 3D chip stacking offers a way to increase computing power and efficiency without solely relying on transistor miniaturization. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of innovation through 3D chip stacking and nanotechnology, the tech industry is on the brink of a new era of computing capabilities. By harnessing the power of these cutting-edge technologies, companies can stay ahead of the curve and maintain their competitive edge in the rapidly evolving market. This shift towards new materials and techniques not only promises increased performance and efficiency but also opens up opportunities for groundbreaking advancements in computing.
## Nanotechnology and Beyond Silicon-based Transistors
Exploring materials and technologies beyond traditional silicon-based transistors, such as nanowires and quantum computing, opens up new avenues for pushing the boundaries of computing performance and capabilities. As companies continue to explore and implement these cutting-edge technologies, the landscape of computing is set to undergo a significant transformation. The potential for increased performance and efficiency not only benefits businesses but also paves the way for revolutionary advancements in various industries. By embracing new materials and techniques, companies can position themselves as leaders in the rapidly evolving market, staying ahead of the curve and maintaining their competitive edge. ### Implications of Reaching the Limits of Moore's Law for the Tech Industry
#### Economic and Market Impact
As Moore's Law begins to hit its limits, the tech industry is poised for a seismic shift. The economic implications are vast, affecting everything from consumer pricing to global market dominance. Companies will need to rethink their strategies as the pace of CPU innovation slows down, potentially leading to a more competitive landscape where differentiation becomes key. As the tech industry grapples with the implications of reaching the limits of Moore's Law, there will be a growing emphasis on efficiency and optimization. Companies will need to explore new ways to maximize the performance of existing technologies, as well as invest in research and development to push the boundaries of what is possible. This shift in focus will require a reevaluation of traditional approaches to innovation and a willingness to embrace new paradigms in order to stay competitive in the evolving landscape.
#### Shifts in Research and Development Focus
With Moore's Law reaching its boundaries, research and development efforts will need to pivot towards alternative avenues for technological advancement. This shift may lead to a renewed focus on areas like quantum computing, neuromorphic engineering, and innovative materials sciences. Companies will need to adapt quickly to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving landscape. As the limitations of Moores Law become more apparent, the need for innovative solutions becomes increasingly urgent. Companies will need to invest in research and development in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy to stay competitive in the market. Collaboration between industries and academia will be crucial in driving forward these new technologies and shaping the future of CPU innovation.
### Future Prospects for CPU Innovation Beyond Moore's Law
#### Exploring Post-Moore's Law Technologies
In a post-Moore's Law era, the spotlight will shift towards exploring new technologies that can drive CPU innovation beyond traditional silicon-based approaches. From quantum computing to DNA computing, the possibilities are endless. Researchers and engineers will need to push the boundaries of what is considered possible to unlock the next wave of breakthroughs. In this new era of CPU innovation, researchers will need to think creatively and experiment with unconventional materials and designs. The race to develop faster, more efficient processors will require a willingness to take risks and explore uncharted territory. As the industry evolves, collaboration will become even more crucial in order to pool resources, share knowledge, and collectively drive progress towards the next generation of computing technology.
Collaboration and Innovation in a Post-Moore's Law Era
As the tech industry navigates the challenges of moving beyond Moore's Law, collaboration will be key. Companies, researchers, and governments will need to work together to foster innovation, share resources, and collectively push the boundaries of what is achievable. The future of CPU innovation lies in the hands of those willing to collaborate and think outside the box.As we stand on the threshold of the limits of Moore's Law, it is clear that the landscape of CPU innovation is undergoing a profound transformation. While challenges and uncertainties lie ahead, the ingenuity and creativity of researchers and engineers continue to drive progress in the field of computing technology. By exploring alternative approaches, embracing new paradigms, and fostering collaboration, the tech industry can navigate beyond the constraints of Moore's Law and usher in a new era of innovation. As we look towards the future, the possibilities for CPU development remain vast, promising exciting advancements that will shape the way we interact with technology for years to come.
Predicting the limits of Moore's Law for future CPU innovation involves understanding both the technical constraints and emerging technologies that could shape the future of semiconductor development. Here's a detailed analysis of where Moore's Law might head and the factors influencing its trajectory:
Understanding Moore’s Law Limits:
**1. Physical Constraints:
- Transistor Miniaturization: As transistors approach atomic scales, quantum effects like electron tunneling become significant, disrupting the ability to scale down further. Current processes are nearing the limits of silicon-based technology.
- Heat Dissipation: Smaller transistors packed into increasingly dense circuits lead to higher power density and heat generation. Efficient cooling solutions become more challenging, impacting overall performance and reliability.
**2. Material and Process Challenges:
- Silicon Limitations: Traditional silicon may not continue to scale effectively. Alternative materials, such as graphene or transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), are being explored, but they come with their own set of challenges and uncertainties.
- Advanced Lithography: Techniques like extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography are pushing the boundaries of what is possible. However, these technologies are complex, costly, and face physical limitations as feature sizes continue to shrink.
**3. Manufacturing Complexity:
- Cost and Yield: The cost of developing advanced semiconductor fabrication facilities is increasing dramatically. Moreover, maintaining high yields becomes more difficult with smaller process nodes, affecting overall feasibility and economic viability.
- Design Complexity: As transistors become smaller, designing and verifying intricate chip layouts becomes increasingly complex, requiring advanced tools and methodologies.
Emerging Technologies and Alternatives:
**1. New Materials and Processes:
- Beyond Silicon: Research into alternative semiconductor materials, such as compound semiconductors and two-dimensional materials, aims to overcome the limitations of silicon.
- Quantum Computing: Though still in the experimental stage, quantum computing promises a fundamentally different approach to processing information, potentially bypassing traditional limitations.
**2. Architectural Innovations:
- 3D Stacking: 3D integration involves stacking multiple layers of transistors to increase density without shrinking feature sizes further. This approach can enhance performance and reduce latency by shortening interconnect distances.
- Chiplets and Modular Designs: Using chiplets—small, modular pieces of silicon that can be combined in various configurations—allows for flexible and scalable designs, addressing some limitations of traditional monolithic chip designs.
**3. Performance Improvements:
- Specialized Processing Units: Focus is shifting towards specialized processing units such as GPUs, TPUs, and FPGAs, which are optimized for specific tasks like AI, machine learning, and parallel processing.
- Heterogeneous Computing: Combining different types of processors (e.g., CPUs, GPUs, and AI accelerators) to optimize performance for specific applications and workloads.
**4. Energy Efficiency:
- Performance per Watt: Improving energy efficiency is becoming increasingly important. Innovations in low-power design, dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), and other power management techniques are essential for maintaining performance while managing power consumption.
Future Outlook:
**1. Continued Evolution:
- Incremental Gains: While traditional scaling may slow, incremental gains in performance and efficiency will continue through architectural advancements, optimization, and new materials.
- Diversification: The focus may shift from pure transistor scaling to a combination of improved architectures, specialized processors, and enhanced efficiency.
**2. Potential Disruptions:
- Quantum and Neuromorphic Computing: These emerging fields could redefine computing paradigms, offering new ways to process information that transcend current limitations.
- Post-Moore’s Law Innovations: As Moore’s Law slows, alternative approaches such as neuromorphic computing, optical computing, and other novel technologies could become more prominent.
Conclusion:
While Moore’s Law may face significant challenges in its traditional form due to physical, material, and manufacturing constraints, innovation in materials, architectures, and efficiency will continue to drive the evolution of CPU technology. The future will likely involve a combination of advanced materials, new computing paradigms, and specialized processors, rather than relying solely on the continued miniaturization of transistors.
What's Your Reaction?