Discussing Challenges Faced by Engineers in Keeping up with Moores Law Expectations for CPUs
Discussing Challenges Faced by Engineers in Keeping up with Moores Law Expectations for CPUs
In the fast-paced world of technology, the expectations for central processing units (CPUs) have been heavily influenced by Moore's Law, which posits that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential advancements in performance. However, the relentless pursuit of meeting these expectations poses significant challenges for engineers in the semiconductor industry. From managing design complexity to addressing power consumption and heat dissipation issues, engineers are confronted with a myriad of obstacles in keeping up with Moore's Law. This article delves into the multifaceted challenges faced by engineers in meeting the evolving expectations for CPUs and explores the strategies and innovations being employed to overcome these hurdles.
Introduction to Moore's Law and Its Impact on CPU Expectations
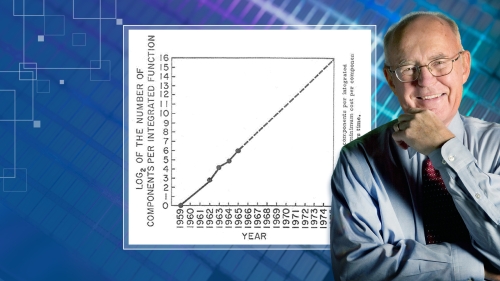
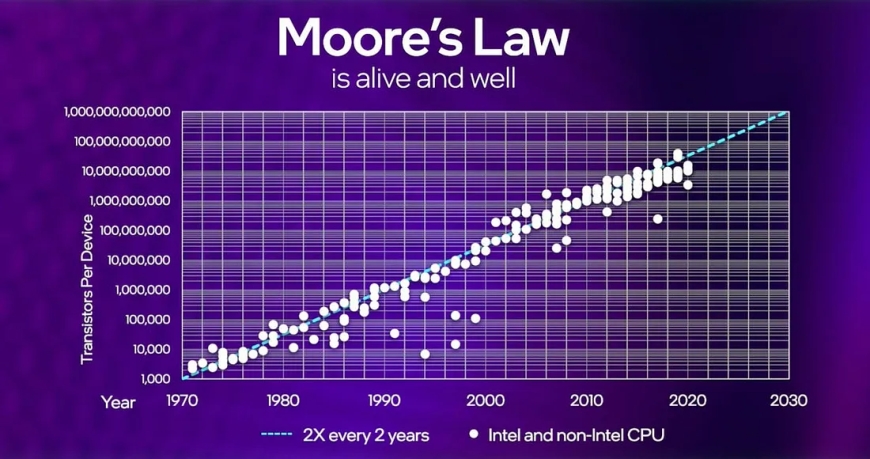
Moore's Law, coined by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in 1965, observes that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power. This law has set the pace for innovation in the tech industry, shaping the expectations for CPU performance and pushing engineers to continuously outdo themselves. Engineers are constantly challenged to keep up with the pace set by Moores Law, as the demand for faster, more efficient CPUs shows no signs of slowing down. This pressure has led to a wave of innovation in the field, with engineers exploring new materials, designs, and architectures to push the boundaries of what is possible. The race to meet and exceed these evolving expectations has fueled a cycle of continuous improvement and breakthroughs in CPU technology.
Understanding Moore's Law and Its Historical Significance

Moore's Law has been the guiding principle behind the rapid advancement of semiconductor technology, driving the development of increasingly powerful and efficient CPUs. Its historical significance lies in revolutionizing the way we perceive technological progress, setting ambitious goals that have propelled the industry forward. The race to meet and exceed these evolving expectations has fueled a cycle of continuous improvement and breakthroughs in CPU technology. Moores Law has been the guiding principle behind the rapid advancement of semiconductor technology, driving the development of increasingly powerful and efficient CPUs. Its historical significance lies in revolutionizing the way we perceive technological progress, setting ambitious goals that have propelled the industry forward.
As Moores Law continues to hold sway over the tech world, the evolution of CPU performance expectations has been nothing short of extraordinary. From single-core processors to multi-core behemoths, engineers have been tasked with exceeding previous limits and delivering cutting-edge CPUs that meet the insatiable demands of modern computing.
In this fast-paced environment, engineers are constantly challenged to innovate and adapt to keep up with the rapid technological advances. The pressure to stay ahead of the curve and deliver groundbreaking solutions has never been greater, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with CPUs.
Evolution of CPU Performance Expectations Driven by Moore's Law
As Moore's Law continues to hold sway over the tech world, the evolution of CPU performance expectations has been nothing short of extraordinary. From single-core processors to multi-core behemoths, engineers have been tasked with exceeding previous limits and delivering cutting-edge CPUs that meet the insatiable demands of modern computing. As engineers strive to keep up with the rapid pace of technological advancements, the pressure to innovate and deliver groundbreaking solutions has never been more intense. The evolution of CPU performance expectations, driven by Moores Law, has forced engineers to constantly push the boundaries of what is possible with CPUs. With the relentless march of technological progress, engineers are faced with the challenge of meeting the insatiable demands of modern computing while also adapting to new technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data.
Rapid Technological Advances and Increasing Demands on Engineers
The relentless march of technological progress has placed ever-increasing demands on engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible with CPUs. With each new advancement in technology, the expectations for CPU performance soar higher, requiring engineers to innovate and adapt at breakneck speed. As engineers strive to keep up with the rapid pace of technological advancements, they must also consider the impact of consumer demand and market trends on CPU development. The need for faster, more powerful CPUs is not only driven by technological advancements, but also by the expectations of consumers who are constantly seeking better performance in their devices. This dual pressure forces engineers to not only innovate in terms of technology, but also in terms of meeting the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Overview of Technological Advancements Driving CPU Expectations
Technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data have fueled the need for faster, more powerful CPUs. Engineers must stay ahead of the curve, anticipating these trends and developing CPUs that can handle the complex computations required to drive these cutting-edge technologies. As engineers strive to push the boundaries of CPU performance to meet the demands of emerging technologies, they must also consider the impact of consumer preferences and market trends. The need for faster, more efficient devices is not only driven by technological advancements, but also by the expectations of consumers who are constantly seeking the latest and greatest products. This dual pressure forces engineers to not only innovate in terms of technology, but also in terms of meeting the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Impact of Consumer Demand and Market Trends on CPU Development
Consumer demand for faster, more efficient devices, combined with market trends favoring performance-oriented products, has put immense pressure on engineers to deliver CPUs that not only meet but exceed expectations. Balancing these demands while staying true to Moore's Law presents a formidable challenge for those in the field. As engineers strive to meet the demands of both consumers and market trends, they are constantly pushing the boundaries of technology to create CPUs that not only perform better but also consume less power and generate less heat. This delicate balance between innovation and practicality is crucial in ensuring that CPUs remain at the forefront of technological advancement. By addressing these challenges head-on, engineers can continue to drive progress in semiconductor technology while also staying true to the principles of Moores Law.
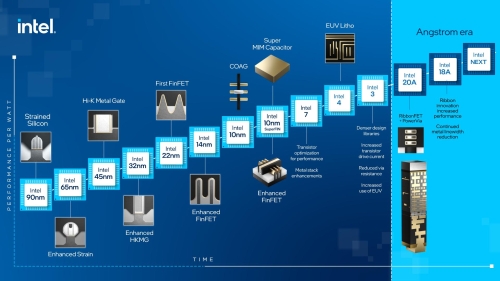
Shrinking Transistor Sizes and the Limits of Semiconductor Technology
The pursuit of ever-smaller transistor sizes has been a central focus of semiconductor technology, but as we approach the limits of miniaturization, engineers are faced with complex challenges that require innovative solutions to keep up with the demands of Moore's Law. As the industry pushes the boundaries of transistor sizes, it becomes increasingly clear that traditional methods may not be sufficient to sustain the pace of technological advancement. Engineers must adapt and innovate to overcome the challenges presented by shrinking transistor sizes, finding new ways to optimize performance while minimizing power consumption and heat dissipation. By embracing alternative approaches and thinking outside the box, the semiconductor industry can continue to push the limits of what is possible in CPU technology.
Challenges and Limitations of Scaling Transistor Sizes
Scaling transistor sizes down to nanometer levels has uncovered challenges related to power consumption, heat dissipation, and quantum effects. Engineers must navigate these limitations to continue delivering CPUs that adhere to Moore's Law's relentless drive for higher performance. As the semiconductor industry grapples with the challenges of scaling transistor sizes and navigating the limitations of traditional technology, it becomes increasingly clear that innovation and creativity are essential for pushing the boundaries of CPU technology. By embracing unconventional methods and thinking outside the box, engineers can unlock new possibilities and drive advancements in performance and efficiency.
Exploring Alternative Approaches to Address Semiconductor Technology Limits
To overcome the barriers posed by the limits of traditional semiconductor technology, engineers are exploring alternative approaches such as novel materials, 3D integration, and quantum computing. These unconventional methods offer new avenues for achieving the performance gains demanded by Moore's Law. As engineers push the boundaries of traditional semiconductor technology, they are met with the daunting task of navigating the intricate landscape of modern CPU design. By embracing unconventional methods and thinking outside the box, they can unlock new possibilities and drive advancements in performance and efficiency. This blend of technical prowess, creativity, and engineering magic is essential in overcoming the challenges posed by the limits of traditional semiconductor technology and the complexities of modern CPU design.
Design Complexity and Integration Challenges in CPU Development
The complexity of modern CPU design and the challenges of seamlessly integrating diverse components present formidable obstacles for engineers striving to keep pace with Moore's Law. Navigating these complexities requires a blend of technical prowess, creativity, and a touch of engineering magic. In order to address these challenges, engineers must constantly innovate and adapt their approaches to CPU development. This requires a deep understanding of the latest technologies and trends in the industry, as well as the ability to think outside the box when faced with complex design issues. By staying ahead of the curve and embracing new methodologies, engineers can effectively manage design complexity and enhance integration efficiency.
Complexity of Modern CPU Design and Integration Processes
As CPUs become more sophisticated, the design processes grow increasingly intricate, involving a myriad of components and subsystems that must work in harmony to deliver optimal performance. Engineers must grapple with this complexity while striving to meet ever-expanding performance expectations. As engineers strive to keep pace with the demands of Moore's Law and deliver ever-faster CPUs, they are faced with the challenge of managing power consumption and heat dissipation. The increasing complexity of modern CPU designs, coupled with the need for higher performance, has led to a surge in power requirements and heat generation. This poses a significant hurdle in meeting performance goals without compromising on energy efficiency and thermal management.
Strategies for Managing Design Complexity and Enhancing Integration Efficiency
To streamline CPU development and enhance integration efficiency, engineers employ strategies such as system-on-chip designs, simulation tools, and modular approaches. By breaking down complex tasks into manageable segments and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, engineers can navigate the intricate landscape of CPU development with finesse.
Power Consumption and Heat Dissipation Issues in Meeting Moore's Law
Impact of Increasing Power Consumption on CPU Development
Picture this: you want your laptop to be faster than a caffeinated cheetah, but it ends up hotter than a thousand suns and slurping power like a smoothie. Yeah, that's the struggle engineers face with Moore's Law. As CPUs get faster and more complex to keep up with our insatiable need for speed, they end up guzzling more power than a thirsty camel in a desert. As power consumption increases, so does the heat generated by the CPU. This heat not only affects the performance of the device but also poses a risk of damaging sensitive components. Engineers are constantly striving to find innovative solutions to balance the need for speed with the challenge of heat dissipation. From advanced thermal management techniques to novel materials that can withstand high temperatures, the race to meet Moores Law while keeping devices cool is a complex and ongoing battle.
Challenges of Heat Dissipation in High-Performance CPUs
Think of your CPU as a hot potato during a game of catch – except it's not fun when it's burning up and slowing down your device. High-performance CPUs generate more heat than an overworked sauna, making heat dissipation a major headache for engineers. Cooling solutions range from fans louder than a rock concert to liquid cooling systems that make your PC feel like a fish tank. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the demand for high-performance CPUs only continues to grow. With this increased demand comes the challenge of effectively dissipating the heat generated by these powerful processors. Engineers are constantly faced with the task of finding innovative and efficient cooling solutions to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance. From advanced thermal management techniques to cutting-edge materials, the race to overcome the heat dissipation challenge is a never-ending battle in the world of high-performance computing.
Strategies and Innovations for Overcoming Engineering Challenges
Exploring Innovative Approaches to Sustain Moore's Law Expectations
Engineers are the MacGyvers of the tech world, constantly tinkering to find innovative solutions to keep up with Moore's Law. From exploring new materials and designs to squeezing every ounce of efficiency from existing technology, they're like wizards trying to pull off a never-ending magic trick with CPUs. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, engineers are faced with the daunting task of not only meeting but exceeding the expectations set by Moores Law. This requires a constant drive for innovation and a willingness to think outside the box. Whether it's through novel approaches to thermal management or the integration of cutting-edge materials, the pursuit of overcoming engineering challenges in high-performance computing is a relentless journey towards pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Collaborative Efforts and Cross-Disciplinary Solutions in Engineering
Just like a superhero team-up in a blockbuster movie, engineers from different fields join forces to tackle the challenges of Moore's Law. Collaborative efforts and cross-disciplinary solutions bring together experts in materials science, computer architecture, and more to push the boundaries of CPU development. It's like a tech Avengers assembling to save the day. As engineers from various disciplines come together to tackle the challenges of Moores Law, innovative solutions are born that push the boundaries of CPU development. By combining expertise in materials science, computer architecture, and more, these collaborative efforts pave the way for groundbreaking advancements in technology. It's a true testament to the power of teamwork and the potential for cross-disciplinary collaboration to drive progress in the field of engineering.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations in Pursuit of Moore's Law
Ethical Implications of Pushing Technological Limits in CPU Development
As engineers push the envelope of CPU performance, ethical questions arise about the impact on society. From concerns about privacy and data security to the widening digital divide, the pursuit of Moore's Law raises important ethical considerations that cannot be ignored. It's like navigating a moral maze in the quest for technological progress. As the demand for faster and more powerful CPUs continues to grow, the pressure to innovate and keep up with Moores Law intensifies. This drive for progress often comes at a cost, with companies racing to develop cutting-edge technology without always considering the ethical implications. It is crucial for engineers and developers to pause and reflect on the potential consequences of their actions, ensuring that advancements in CPU development are made responsibly and with the well-being of society in mind.
Environmental Impact of Semiconductor Manufacturing and Disposal
Behind every powerful CPU lies a trail of electronic waste and environmental impact. The semiconductor manufacturing process is not exactly eco-friendly, with harmful chemicals and massive energy consumption. Engineers need to balance technological advancement with environmental sustainability to ensure that future generations don't inherit a digital wasteland. As the demand for faster and more powerful CPUs continues to grow, so does the need for sustainable manufacturing and disposal practices. Companies in the semiconductor industry are under increasing pressure to find innovative solutions that minimize environmental impact while still meeting the demands of consumers. It is crucial for engineers to not only focus on technological advancement, but also on finding ways to reduce waste and energy consumption in the production process.
The Future of CPU Development and Adaptation to Changing Technology Trends
Anticipated Trends in CPU Development Beyond Moore's Law
Moore's Law may be like that trusty old friend who's been around forever, but the future of CPU development is a wild ride into uncharted territory. As we approach the limits of silicon-based computing, new technologies like quantum computing and neuromorphic engineering are knocking on the door, ready to revolutionize the way we think about CPUs. As we navigate this new era of CPU development, engineers must not only focus on pushing the boundaries of technological advancement but also on finding sustainable solutions to reduce waste and energy consumption in the production process. The shift towards more efficient and eco-friendly practices will be essential in ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from the incredible advancements in computing power. By embracing these challenges and opportunities, engineers can pave the way for a more sustainable and innovative future in CPU development.
Adapting Engineering Practices to Embrace Future Technological Shifts
To stay ahead in the ever-evolving tech landscape, engineers need to be as adaptable as chameleons at a color wheel convention. Embracing future technological shifts means constantly learning, innovating, and being open to change. The future of CPU development is like a sci-fi novel waiting to be written, and engineers are the authors shaping the next chapter.As engineers continue to push the boundaries of technological advancement to meet Moore's Law expectations for CPUs, it is evident that a collaborative and innovative approach is essential in navigating the complex challenges that lie ahead. By embracing sustainability, ethical considerations, and forward-thinking solutions, the future of CPU development holds promising opportunities for progress and adaptation to the ever-changing landscape of technology. With a steadfast commitment to innovation and problem-solving, engineers are poised to meet the demands of tomorrow's computing needs and shape the future of semiconductor technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Moore's Law and how does it impact CPU development?
Moore's Law is a principle that states the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential improvements in CPU performance. This rapid advancement sets high expectations for engineers in developing CPUs that can keep up with the pace of technological growth. As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the pressure on engineers to meet Moores Law expectations for CPUs only intensifies. With the demand for faster, more efficient processors constantly on the rise, the need for groundbreaking advancements in chip design becomes paramount. This constant push for innovation drives the industry forward, challenging engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible in CPU development.
What are some of the key challenges engineers face in meeting Moore's Law expectations for CPUs?
Engineers encounter challenges such as managing increasingly complex design processes, addressing power consumption and heat dissipation issues, and navigating the limits of semiconductor technology as transistor sizes shrink. These obstacles require innovative solutions and strategic approaches to sustain the pace of CPU development. As the demand for faster and more efficient CPUs continues to grow, engineers are also facing the challenge of balancing performance with cost-effectiveness. This requires a careful consideration of trade-offs and compromises in design decisions, as well as a focus on optimizing resources and maximizing efficiency. Additionally, the increasing complexity of software applications and the rise of artificial intelligence are driving engineers to explore new architectures and paradigms to meet evolving computational needs.
How are engineers adapting to the changing landscape of CPU development beyond Moore's Law?
Engineers are exploring alternative approaches to traditional semiconductor technology, collaborating across disciplines to drive innovation, and considering ethical and environmental implications in their pursuit of efficiency and sustainability. By embracing new trends and technologies, engineers are preparing for the future of CPU development beyond the constraints of Moore's Law. Some engineers are focusing on developing new materials and architectures to overcome the limitations of Moores Law, while others are exploring quantum computing and neuromorphic computing as potential alternatives. Additionally, engineers are also looking into ways to optimize energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of CPU development, ensuring a more sustainable future for technology advancement.
What's Your Reaction?