An overview of how heat is transferred and dissipated in a water-cooled system
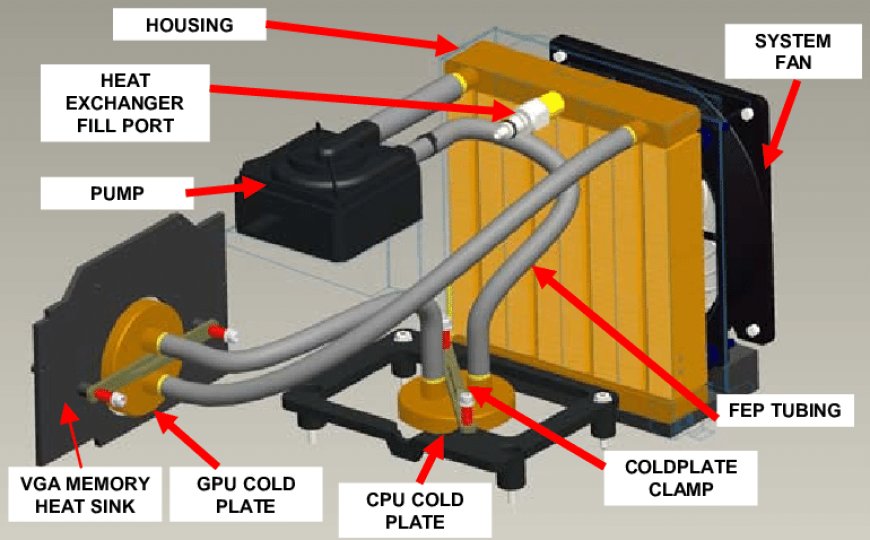
An overview of how heat is transferred and dissipated in a water-cooled system
Heat transfer and dissipation play a crucial role in the efficient operation of water-cooled systems, which are widely used in various industrial and commercial applications. Understanding the mechanisms by which heat is transferred and dissipated is essential for optimizing the performance and longevity of such systems. In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles of heat transfer in water-cooled systems, the different types of heat transfer mechanisms involved, the key components of these systems, and the factors that influence heat transfer efficiency. Additionally, we will examine the importance of monitoring and maintaining optimal heat dissipation in water-cooled systems, as well as the advantages and challenges associated with this cooling method.
### An Overview of How Heat is Transferred and Dissipated in a Water-Cooled System
#### 1. Introduction to Heat Transfer in Water-Cooled Systems
##### Understanding the Basics of Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is like the matchmaking of the thermal world: getting hot molecules to cozy up with cooler ones. Heat dissipation in water-cooled systems is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the system. Without proper dissipation, heat can build up and lead to overheating, which can damage components and reduce performance. By effectively dissipating heat, water-cooled systems can operate at optimal temperatures, ensuring smooth and reliable performance.
##### Importance of Effective Heat Dissipation
Think of heat dissipation as giving your devices a breather—without it, they would throw a tantrum hotter than a summer day in the desert. Effective heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining the longevity and performance of electronic devices. Without proper dissipation, heat can build up and lead to overheating, which can damage components and reduce performance. By effectively dissipating heat, water-cooled systems can operate at optimal temperatures, ensuring smooth and reliable performance. Think of heat dissipation as giving your devices a breather—without it, they would throw a tantrum hotter than a summer day in the desert.
When it comes to heat transfer mechanisms, conduction, convection, and radiation play key roles in keeping systems cool. Conduction is like a game of telephone but with atoms passing hot gossip, convection is when hot air gets adventurous, and radiation is heat's way of saying, "I'll find you no matter what." Specific applications in water-cooled systems highlight how conduction acts as water's way of playing messenger, convection showcases its dance moves, and radiation demonstrates its cool charisma.
#### 2. Types of Heat Transfer Mechanisms
##### Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Conduction is like a game of telephone but with atoms passing hot gossip, convection is when hot air gets adventurous, and radiation is heat's way of saying, "I'll find you no matter what. Heat transfer mechanisms play a crucial role in the efficiency of water-cooled systems. Conduction, convection, and radiation each have their own unique characteristics that contribute to the overall cooling process. By understanding how these mechanisms work together, engineers can optimize the performance of water-cooled systems to ensure effective heat dissipation. "
##### Specific Applications in Water-Cooled Systems
In water-cooled systems, conduction is water's way of playing messenger, convection is its dance moves, and radiation is its cool charisma. When it comes to water-cooled systems, conduction is like the steady beat of a drum, transferring heat from one point to another with precision. Convection, on the other hand, is the fluid movement that keeps the heat flowing smoothly throughout the system. And radiation? Well, radiation is the subtle touch of elegance that adds a touch of finesse to the entire cooling process.
#### 3. Components of a Water-Cooled System
##### Heat Sources and Heat Sinks
Heat sources are like the overexcited guests at a party, while heat sinks are the chill friends who help regulate the vibe. When it comes to a water-cooled system, the components work together like a well-oiled machine. Heat sources generate the heat, while heat sinks efficiently dissipate it, creating a harmonious balance. The cooling medium, water, plays a crucial role in carrying away the heat, with the circulation system ensuring that the process is seamless and effective.
##### Cooling Medium and Circulation System
The cooling medium is water’s runway, strutting its stuff to dissipate heat, while the circulation system is its posse, making sure the coolness spreads like wildfire. Heat sources generate the heat, while heat sinks efficiently dissipate it, creating a harmonious balance. The cooling medium, water, plays a crucial role in carrying away the heat, with the circulation system ensuring that the process is seamless and effective. Water acts as a versatile medium, able to absorb and transfer heat efficiently, while the circulation system ensures that the cool water reaches every part of the system, leaving no hot spot untouched.
#### 4. The Role of Water in Heat Dissipation
##### Advantages of Water as a Cooling Medium
Water is like the superhero of cooling, swooping in to save the day with its high heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Water acts as a versatile medium, able to absorb and transfer heat efficiently, while the circulation system ensures that the cool water reaches every part of the system, leaving no hot spot untouched. Water is like the superhero of cooling, swooping in to save the day with its high heat capacity and thermal conductivity. In a cooling system, water plays a crucial role in dissipating heat generated by various processes, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. The efficient heat transfer properties of water make it an ideal choice for cooling applications, providing a reliable and effective solution for managing thermal loads.
##### Water Circulation Methods in Cooling Systems
Water circulation is like a well-orchestrated ballet, ensuring every nook and cranny gets its cool moment in the spotlight. Water circulation methods in cooling systems are essential for maintaining the efficiency of heat transfer. Whether it's through natural convection, forced convection, or a combination of both, the goal is to ensure that heat is effectively carried away from the hot components. Just like a well-choreographed dance, the circulation of water must be carefully orchestrated to reach every part of the system and keep temperatures in check. # 5. Factors Influencing Heat Transfer Efficiency
## Temperature Differentials and Thermal Conductivity
Think of temperature differentials as the spicy factor in your heat transfer soup. The bigger the temperature difference between the hot components and the cooling water, the faster heat will move away. Additionally, thermal conductivity plays a crucial role in this heat dance - materials like copper conduct heat like a rock star on stage, while others might be a bit more shy. When it comes to heat transfer efficiency, it's not just about the temperature differentials and thermal conductivity. The design and layout of the heat transfer system also play a significant role. Factors such as the distance between the hot components and the cooling water, the material of the heat exchanger, and the overall efficiency of the system can all impact how effectively heat is transferred. Additionally, proper insulation and maintenance of the system can help prevent heat loss and improve overall efficiency.
## Flow Rate and Surface Area for Heat Exchange
Imagine a highway during rush hour - the more lanes (surface area) your cooling system has, the smoother the traffic (heat exchange) will flow. Similarly, the speed at which the cooling water flows through the system (flow rate) can make a big difference in how quickly heat gets whisked away. When it comes to maximizing the efficiency of your cooling system, finding the right balance between flow rate and surface area is key. Just like a well-planned highway system, ensuring that your system has enough surface area for heat exchange and a sufficient flow rate for efficient cooling can make a significant impact on overall performance. By carefully monitoring and adjusting these factors, you can ensure that your system operates at peak efficiency and avoids any potential overheating issues.
# 6. Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal Heat Dissipation
## Temperature Sensors and Cooling System Controls
Temperature sensors are like the loyal guardians of your system, constantly keeping an eye on the heat levels. With proper cooling system controls, you can adjust the flow rate or fan speed to maintain optimal temperatures and prevent overheating catastrophes. When it comes to monitoring and maintaining optimal heat dissipation, it's crucial to stay proactive in your approach. Regularly checking and cleaning your system's components, such as radiators and water blocks, can help ensure efficient heat transfer and prevent any potential issues from arising. By staying on top of maintenance tasks, you can extend the lifespan of your cooling system and avoid costly repairs down the line.
## Regular Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Just like giving your car an oil change, regular maintenance is key to keeping your water-cooled system purring like a contented kitten. Keep an eye out for leaks, clogs, or any signs of trouble, and address them promptly to avoid a meltdown. When it comes to troubleshooting, it's important to not only address issues promptly but also to regularly check and clean your system to prevent problems from arising in the first place. By staying proactive and attentive to your water-cooled system, you can ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
# 7. Advantages and Challenges of Water Cooling Systems
## Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Water cooling systems can be the eco-warrior of the cooling world, using less energy compared to traditional air cooling methods. However, they do require a constant water supply, which can raise concerns about water usage and potential environmental impacts. Water cooling systems offer a more efficient way to dissipate heat, making them a popular choice for high-performance computing systems. The ability to remove heat more effectively can also lead to longer equipment lifespan and improved overall performance. However, it is important to carefully monitor and maintain water cooling systems to ensure they continue to operate at peak efficiency.
## Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
While water cooling systems can be super effective, they also come with their own set of risks, like leaks or corrosion. Mitigation strategies such as using corrosion inhibitors, regular inspections, and having backup plans in place can help prevent these risks from turning into a soggy mess.In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of how heat is transferred and dissipated in water-cooled systems is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and efficiency. By recognizing the role of water as a cooling medium, monitoring key factors influencing heat transfer efficiency, and addressing maintenance requirements, users can ensure the optimal performance of their water-cooled systems. Despite the challenges that may arise, the advantages of using water cooling, such as energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, make it a valuable choice for various cooling applications. By implementing best practices and staying informed on advancements in heat transfer technology, users can continue to benefit from the effectiveness of water-cooled systems in the future.
What's Your Reaction?